Fibroid Embolization
 What are Fibroid Tumors?
What are Fibroid Tumors?
Fibroids are non-cancerous (benign) growths that develop in the muscular wall of the uterus. They usually aren't life threatening, but they can be life altering. For the forty percent of women over age forty who have them, fibroids can cause prolonged heavy menstrual periods, severe cramping, incontinence and a host of other problems. Hysterectomy has been the most common treatment for these growths.
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) is the New Non-Surgical Approach
Fibroid embolization, also called uterine artery embolization, is a proven effective alternative for treating fibroids without surgery. It requires only a tiny nick in the skin about the size of a pencil tip. It is performed while the patient is conscious, but lightly sedated.
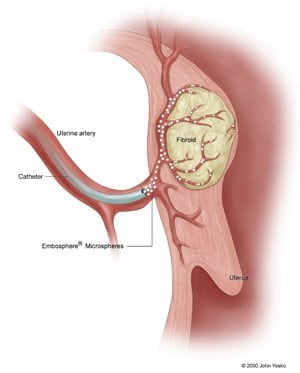
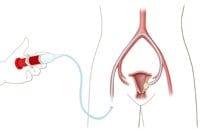 An interventional radiologist is a physician specially trained to perform this and other minimally invasive procedures. The interventional radiologist makes a small nick in the skin in the groin, through which a tiny tube called a catheter is inserted into an artery. The catheter is guided through the artery to the uterus while the interventional radiologist watches the progress of the procedures using a moving x-ray (fluoroscopy.)
An interventional radiologist is a physician specially trained to perform this and other minimally invasive procedures. The interventional radiologist makes a small nick in the skin in the groin, through which a tiny tube called a catheter is inserted into an artery. The catheter is guided through the artery to the uterus while the interventional radiologist watches the progress of the procedures using a moving x-ray (fluoroscopy.)
When the catheter is in place, the interventional radiologist injects tiny plastic or gelatin sponge particles the size of grains of sand into the artery that supplies blood to the fibroid tumor. The particles form a "logjam" in the artery, cutting off the blood flow to the fibroid and causing it to shrink.
Time Required
Fibroid embolization usually requires a hospital stay of one night. Total recovery generally takes one to two weeks, but sometimes can take longer.
Associated Risks
Fibroid embolization is considered to be very safe, but there are some associated risks as there are with any procedure. These risks include:
- A small number of patients age 45 and older reportedly enter into menopause after embolization
- Possible infertility
- Future fibroid interventions may be required
Images provided courtesy of BioSphere Medical Inc. (now Merit Medical Systems).
